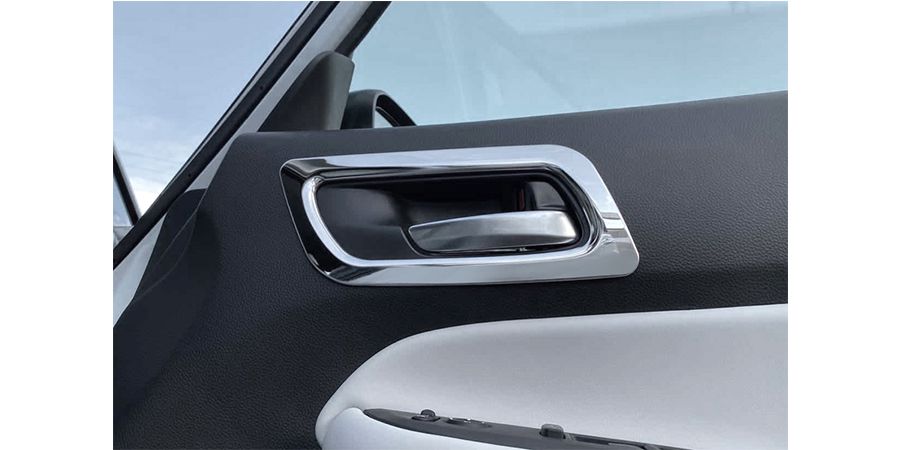
With the development of the economy, there are more and more decorative parts on the car, especially the trim strips, which can enhance the overall interior atmosphere and grade.
Decorative strips are used in almost every corner of the car as interior decoration parts. Have you noticed it in your car? Here is a brief list of several common application areas of decorative strips:
Decorative strips are used in so many places, so, what kind of process are used to form these decorative strips? Today, I will introduce three more mature trim crafts that are currently used in interior decorations.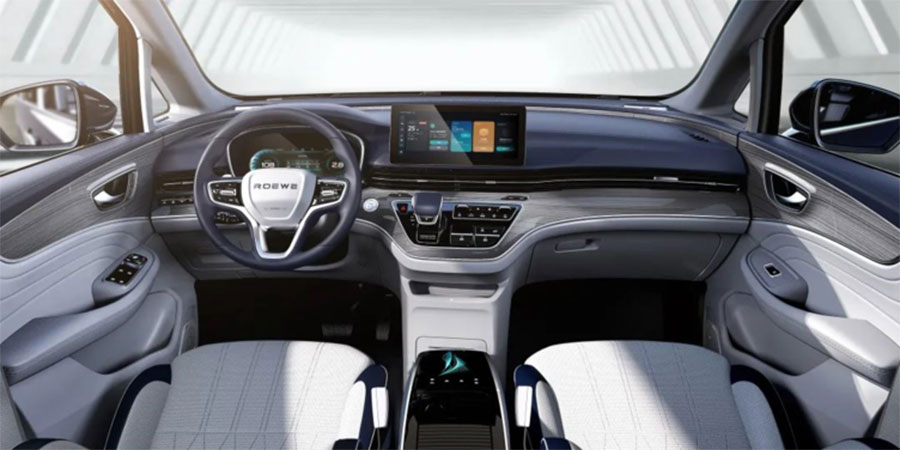
IMD (In-Mold Decoration) is an internationally popular surface decoration technology. IMD is actually just a general term. IMD generally includes IMR, IML, INS, etc. At present, it is customary in the industry to call IMR as IMD.
IMR (In-Mold Roller) means in-mold transfer: it consists of four steps: film transfer, film adsorption, injection molding and product removal. Usually, the continuous IMR film roll is installed on the film conveying machine, and the film conveying machine is fixed on the injection molding machine. When the injection mold is opened, the film is fed into the middle of the mold, and the ink pattern is transferred to the plastic after the mold is closed for injection.
IMR has only one set of injection molds, which has low cost, simple process, high efficiency, small stretching deformation, and can achieve a variety of pattern effects; the disadvantage is that the product shape requirements are relatively strict, and the molding surface cannot be complicated or stretched. Large parts.
Second, the “INS” process of decorative strips
INS (Insert-Mold Decoration) is the insert injection molding process: as shown in the figure, three sets of molds respectively complete the film suction, film punching and film injection processes. Usually, using the method of thermoforming or high-pressure forming, the transferred ABS sheet is stretched three times, and then the insert is cut out according to the product shape, and then the insert is accurately placed in the injection mold cavity Injection molding.
The INS process can realize more complex product shapes, regular patterns are easy to stretch, less deformed, and can achieve a certain touch (such as a very strong 3D texture) and imitation solid wood effect; but the overall cost is high, the production process is complex, and the efficiency is low. The defect rate is high.
IML (In-Mold Label) is the in-mold insert injection molding process. The printed decorative sheet is placed in the injection mold, and then the resin is injected into the ink layer on the back of the molded sheet to connect the resin to the sheet. Combining the technology of one-piece curing and molding. Three sets of molds respectively complete the stretch forming, punching and injection processes. The production steps of IML and INS decorative strips are the same, the difference is the difference in the composition of the diaphragm.
The IML process can achieve simple precise positioning, and can achieve a slightly deeper shape than IMD, and the price is lower than that of INS; the disadvantage is that it can only achieve simple geometric patterns, and cannot achieve complex patterns such as wood grain, and the fineness of the pattern is poor, and the size Larger products are difficult to realize, and the production process is complex and low in efficiency.
In summary, the structure, composition, geometric size and price of the three types of diaphragms are compared as follows, and the corresponding process can be selected for car interior decoration according to actual needs.
In terms of geometry: the side coating depth INS>IML>IMD, but it is difficult to achieve IML for products with larger and complex shapes;
Product price: Under the premise of the same effect and size, INS>IML>IMD; in the case of a single-color and simple shape product, the price of IML may be slightly lower than IMD.